

Google Patents Unijunction transistor oscillator circuitĭownload PDF Info Publication number US3202937A US3202937A US267406A US26740663A US3202937A US 3202937 A US3202937 A US 3202937A US 267406 A US267406 A US 267406A US 26740663 A US26740663 A US 26740663A US 3202937 A US3202937 A US 3202937A Authority US United States Prior art keywords resistor capacitor unijunction transistor base zener diode Prior art date Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google Patents US3202937A - Unijunction transistor oscillator circuit In addition, UJTs are widely used to provide clock for digital circuits, timing control for various devices, controlled firing in thyristors, and sync pulsed for horizontal deflection circuits in CRO.US3202937A - Unijunction transistor oscillator circuit They are also used in Phase Control Circuits. UJTs are most prominently used as relaxation oscillators. The region after this is termed as Saturation region. The voltage at this point is called as V V ( Valley Voltage) and the current at this point is called as I V ( Valley Current). Now, the voltage V E reaches a certain point where further increase leads to the increase in voltage across R B1.
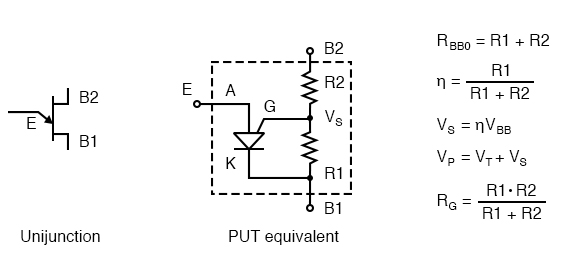
This is the Negative resistance property and hence this region is called as Negative resistance region. Now, when V E is further increased, the resistance R B1 and then the voltage V 1 also decreases, but the current through it increases. The portion in the graph till now, is termed as Cut off region as the UJT was in OFF state. The voltage at this point is called as V P ( Peak Voltage) and the current at this point is called as I P ( Peak Current). This is the point where the curve touches the Y-axis.Īt this point, the diode gets forward biased. Initially when V E is zero, some reverse current IE flows until, the value of VE reaches a point at which The concept discussed till now is clearly understood from the following graph shown below. The voltage at which the UJT gets switched ON is the Peak Voltage denoted as V P. It decreases to a least value which may be denoted V V called as Valley voltage. So, this is constant and V B1 goes on decreasing. Where V D is the voltage across the diode.Īs the diode gets forward biased, the voltage across it will be 0.7v. Hence voltage across V B1 is represented as The symbol η is used to represent the total resistance applied. Therefore, the potential across R B1 which means V B1 also decreases. The carriers get induced and the resistance R B1 goes on decreasing. This current makes the diode forward biased. Now if the emitter voltage V E is increased, the current I E flows through the diode D. Due to the application of V BB, some voltage appears at point A. The voltage across the diode will be VB which is the barrier voltage of the emitter diode. Then the voltage V BB is applied through R B2. The UJT equivalent circuit is as given below. The dc voltage applied for the circuit to function is V BB. The voltage across RB1 can be denoted as V 1. Both resistances present internally are together called as intrinsic resistance, indicated as R BB. The voltage applied at the emitter is indicated as V E and the internal resistances are indicated as R B1 and R B2 at bases 1 and 2 respectively. The working of UJT can be understood by its equivalent circuit.
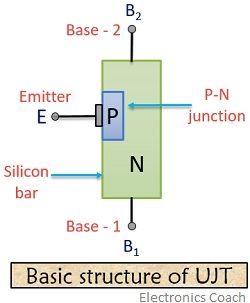
As the UJT is understood as a combination of diode and some resistance, the internal structure of UJT can be indicated by an equivalent diagram to explain the working of UJT. In the symbol, the emitter is indicated by an inclined arrow and the remaining two ends indicate the bases. The construction and symbol of UJT are as shown below. As single PN junction is present, this component is called as a Unijunction transistor.Īn internal resistance called as intrinsic resistance is present inside the bar whose resistance value depends upon the doping concentration of the bar. Both of these join to form a PN junction. This emitter lies near to the base 2 and a bit far to the base1. An aluminum rod like structure is attached to it which becomes the emitter. Two Ohmic contacts are drawn at both the ends being both the bases. Construction of UJTĪ bar of highly resistive n-type silicon, is considered to form the base structure. This component is especially famous for its negative resistance property and also for its application as a relaxation oscillator. Unijunction Transistor, or simply UJT has an emitter and two bases, unlike a normal transistor. Unijunction Transistor is such a transistor that has a single PN junction, but still not a diode.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
